The IMF managing director, Christine Lagarde. / EFE
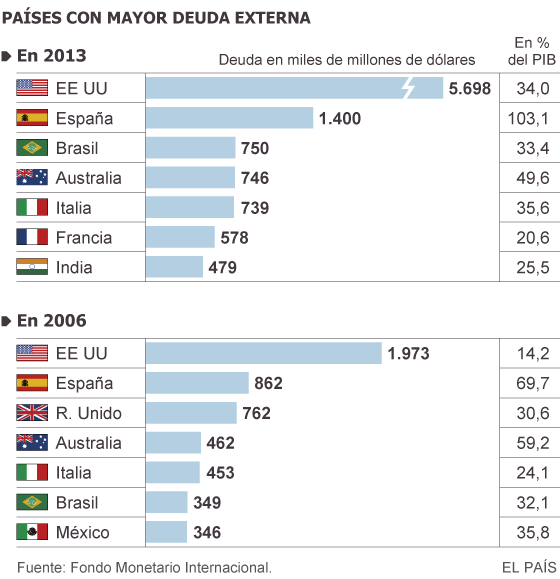
The United States alone exceeds Spain as a country with a larger volume of debt to external creditors dependent. American foreign debt is the most substantial in the world, with about 5.5 billion dollars at the end of 2013, while Spain is next with 1,400 million. But there is a difference in weight between the first and second: for the USA, these foreign credits account for 34% of its gross domestic product (GDP), while for the Spanish accounts for 103% of its economy. The data comes from Chapter 4 of the new global report estimates that the International Monetary Fund (IMF) presented next week in Washington and warns of the need to further reduce such imbalances.
“Systemic risks from global imbalances have declined,” admits IMF, but “reduce external loans creditor economies requires improvements in the current account balances and stronger growth.” But this need for a more balanced economic expansion (and strongly backed by external or too dependent on domestic demand) affects not only the deficit countries, but also those who have “margin thanks to its powerful surpluses” warns organism week prior to their fall general assembly.
The Fund has already urged Germany, part of this group, without much success to boost their investments to boost the economy.
In the list of the world’s biggest creditors are Japan ($ 3 billion) and China (1.6 billion), which before the great financial storm in 2006, occupied the seventh place in the same classification. Germany, which was the second this year, ended 2013 as the third great world creditor, with $ 1.6 trillion foreign rendered.
the United States and Spain, however, were already the most indebted abroad before the crisis. The IMF says that drastic cuts in the economic outlook of the biggest post-crisis debt reduced value of the assets in them, something that despite imply a negative effect on the country’s wealth, it also means a lower value for their foreign loans, representing a capital gain. “USA was unique in this: despite being the most indebted and have a great downward revision of growth prospects, the value of assets increased due to the concern for finding safe havens, implying a capital loss in its international investment position. “
The global imbalances have declined by about a third between 2006 and 2013, as some large current account deficits, such as USA, or surpluses, such as China have been narrowed, but “surpluses in some countries of the hard core of the eurozone, however, have remained large,” says the Fund, also in emerging markets have deteriorated.
More public investment in infrastructure
The IMF, which is facing its assembly with fully standing and emerging powers such as Brazil euro zone into recession, the report also addresses global perspective the need to rely on public investment support infrastructure. “The borrowing costs are low and demand is weak in advanced economies and many emerging markets and developed economies there are limitations in infrastructure,” the report said.
The problem with the recipe is of the disparate scenarios. Spain, for example, leaves behind a infraesutructuras time investment that will be remembered words linked to excess and waste, as many great works have shown then unnecessary, very iconic images, including the Castellón airport not it has been brand new.
“An increase of 1% of GDP in infrastructure investment increases the level of output around 0.4% in the same year and about 1.5% in the next four years, “he said at a press conference Abdul Abiad, deputy head of the Research Division of the IMF.
The IMF proposal adheres to countries with” special needs “in public infrastructure, which are an “indispensable contribution” to economic output, which is also highly complementary with other contributions such as employment and (no corresponding infrastructure) private capital.
In this regard, the institution emphasizes that is “difficult to think of a production process in any sector that is not dependent infrastructure” and emphasizes that any deficiency is felt quickly. “Energy Cortes, inadequate water supply or rough roads adversely affect the quality of life of the people and impose significant for the work of enterprises barriers,” he says.





